what happens to e. coli during and mr/vp test|3.8: Methyl Red : Pilipinas Describe the purpose and usefulness of the MR-VP test. Compare and contrast the MR test and the VP test. Tell how the MR test and VP test are conducted and what the results mean. Define fermentation and describe its importance. . Join Date 6 Aug 2022 Posts 28,886. GirlsDoPorn - E543 - 19 Years Old [09 27 19] Name: GirlsDoPorn - E543 - 19 Years Old [09 27 19] Format: mp4 Size: 787.69 MB
what happens to e. coli during and mr/vp test,Principle of Voges–Proskauer (VP) Test. The Voges-Proskauer (VP) test is used to determine if an organism produces acetylmethyl carbinol . In the methyl red test (MR test), the test bacteria is grown in a broth medium containing glucose. If the bacteria has the ability to utilise glucose with production of a stable acid, the color of the methyl red changes from .what happens to e. coli during and mr/vp testDescribe the purpose and usefulness of the MR-VP test. Compare and contrast the MR test and the VP test. Tell how the MR test and VP test are conducted and what the results mean. Define fermentation and describe its importance. .If present, acetylmethylcarbinol is converted to diacetyl in the presence of α-naphthol, strong alkali (40% KOH), and atmospheric oxygen. The diacetyl and guanidine-containing compounds found in the peptones of the broth then .
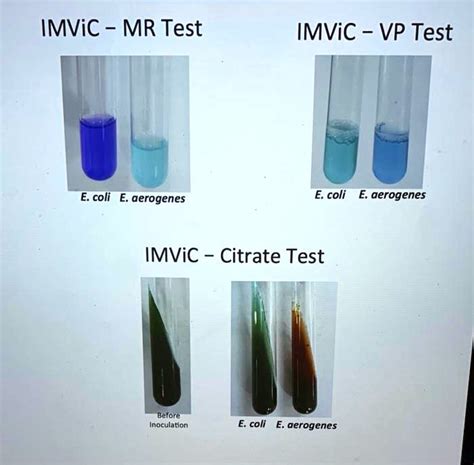
VP test is a biochemical test that detects the ability of bacteria to metabolize the pyruvate into a neutral intermediate product called ‘acetylmethylcarbinol’ or ‘acetoin’.what happens to e. coli during and mr/vp test 3.8: Methyl Red VP test is a biochemical test that detects the ability of bacteria to metabolize the pyruvate into a neutral intermediate product called ‘acetylmethylcarbinol’ or ‘acetoin’.Escherichia coli is MR+ and VP-. In contrast, Enterobacter aerogenes and Klebsiella pneumoniae are MR- and VP+. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a glucose nonfermenter and is thus MR- and VP-.
Methyl red test, commonly known as MR test is used to determine the ability of an organism to produce and maintain stable acid end products from glucose fermentation. MR .
Methyl red is a pH indicator. In the presence of highly acidic conditions, as generated by mixed acid fermenters, the indicator appears read (Fig. 1). As the pH rises, i.e., becomes alkaline, . MR: If the tube turns red, the test is positive for mixed acid fermentation (one or more organic acids formed during the fermentation of glucose). VP: If the tube (or interface) .

In order to test this pathway, an aliquot of the MR/VP culture is removed and a-naphthol and KOH are added. They are shaken together vigorously and set aside for about one hour until the results can be read. . Escherichia coli is MR+ .
MR-VP test stands for Methyl Red -Voges Proskauer Test. It will be discussed in two tests separately. . Escherichia coli ATCC 25922—MR positive(red),VP negative(no change) Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883—MR negative (yellow), VP positive . Observe for a pink-red color at the surface within 30 min. Shake the tube vigorously during the .Indole test; Methyl red (MR) test; Voges-Proskauer (VP) test; Citrate utilization test; Three test tubes are inoculated to obtain the results of these four tests: tryptone broth (indole test), methyl red – Voges Proskauer broth (MR-VP .3.8: Methyl Red Tryptophanase catalyzes the deamination reaction, during which the amine (-NH2) group of the tryptophan molecule is removed. Final products of the reaction are indole, . In enteobacteria test we are not getting e.cold recovery where as individual e.coli test showing growth in suitability test.what might be the reason. Reply. shaima fuaf .indicative of a positive VP reaction. The absence of a red color is considered a negative VP result. It is generally true that a MR positive enteric species is VP negative, and vice versa. Figure 1. Methyl Red Test Using MR-VP Media. The left image depicts the positive methyl read reaction of Escherichia coli. The right image shows the negative . This test demonstrate the presence of catalase, an enzyme that catalyses the release of oxygen from hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2).It is used to differentiate those bacteria that produces an enzyme catalase, such as staphylococci, from non-catalase producing bacteria such as streptococci.Normally 3% H 2 O 2 is used for the routine culture while 15% H 2 O 2 is used . VP negative organisms are: E. coli, Streptococcus mitis, Citrobacter sp., Shigella, Yersinia, Edwardsiella, Salmonella, Vibrio furnissii, Vibrio fluvialis, Vibrio vulnificus, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus ** Both MR and VP positive organisms: Hafnia spp, Proteus spp, Serratia spp Precautions: The culture must be incubated nit less than 48 hours; The reagents should be .

Aseptically inoculate each test tube with the test microorganism using an inoculating needle or loop. Alternatively, inoculate each test tube with 1-2 drops of an 18- to 24-hour brain-heart infusion broth culture of the desired organism. Incubate tubes at 35-37°C for 18-24 hours. Check for color changes or formation of gas. Result Interpretation
The Voges-Proskauer (VP) test detects organisms that utilize the butylene glycol pathway and produce acetoin during glucose metabolism. After inoculation and incubation of the enterotube, the production of acetoin is detected using Barritt’s reagent (potassium hydroxide, and alpha-naphthol) in the VP chamber.
E. coli is a dangerous food-borne bacteria that could lead to death. In order to test for E. coli, a methyl red test can be performed. This test indicates the presence of mixed acid fermentation .MR Test: the acids made by e coli are strong enough to over the buffering of phosphate which will do what? . What happens over time? positive = dark red band at the top and over time will diffuse into the media. can an organism be positive for both MR and VP test? No. Sets with similar terms. Microbiology *(Catalase)* 79 terms. NurseLife40 . Obtain one tube of MR-VP broth. Using an inoculating loop, swish some of your assigned organism in the broth; Incubate the tube for at least 48 hours. After the incubation period, vortex the tube and pour half of the broth into another clean test tube. Complete the tests on the two individual tubes as follows: Our lake has been tested for E. Coli and the results were given as such: 1: >80. 2: 5. 3: 5. and 4: 55. I assume they did 5 separate tests but did not explain if these are high or low and whether our is contaminated to the . Principle of Methyl Red (MR) Test. Methyl red test, commonly known as MR test is used to determine the ability of an organism to produce and maintain stable acid end products from glucose fermentation. MR test along with the VP test is performed simultaneously because they are physiologically related and are performed on MRVP broth. All members .
Detection and Identification of E. COLI. E. coli is an aerobe, rod-shaped, motile, Gram-negative intestinal bacterium that ferments lactose and other carbohydrates (Table 1).Detection is possible because the bacterium ferments dextrose (D-glucose) by producing mixed acids (e.g., lactic, acetic, and formic acids) that is made visible with the addition of methyl red indicator.
Fermentation Test. In this experiment, fermentation of two different carbohydrates will be tested: glucose and lactose. Label three phenol red glucose tubes each with a species names to be tested (Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Proteus vulgaris), group name, and medium name.Repeat for three phenol red lactose tubes.
8. Using a glass Pasteur pipet, take 1 ml out of your MR-VP broth tube and place it into a new tube. 9. Add 5 drops MR methyl red reagent to the new tube, record results (positive result = red) 10. Using a glass pipet take 1 ml out of MR-VP broth tube and place it into a new tube. 11. Add 6 drops VP-A and 3 drops VP-B, record results (positive . During the test, the organisms utilize urea as the sole source of nitrogen, producing a sufficient amount of ammonia to overcome the buffering capacity of the medium. . Negative test: Escherichia coli. Uses of Urease Test. Urease test is used to identify organisms that are capable of hydrolyzing urea to produce ammonia and carbon dioxide.
what happens to e. coli during and mr/vp test|3.8: Methyl Red
PH0 · Voges–Proskauer (VP) Test
PH1 · Voges Proskauer (VP) Test: Principle, Procedure, Results
PH2 · Voges Proskauer (VP) Test: Principle, Procedure,
PH3 · VP Test: Principle, Reagents, Procedure, Results,
PH4 · Methyl Red (MR) Test: Principle, Procedure, and Results
PH5 · Methyl Red (MR) Test
PH6 · MRVP test
PH7 · METHYL RED
PH8 · 3.8: Methyl Red
PH9 · 1.27: MR